- Rise of Sex Dolls: Technology and Market Growth
- Legal and Ethical Controversies Worldwide
- Understanding Sex Doll Legality: Global Overview
- North American Sex Doll Legislation
- European Sex Doll Laws
- Asia-Pacific Sex Doll Regulations
- Middle East, Africa, and Other Regions
- Key Legal Issues and Prohibited Features
- Consumer Guide: Ensuring Legal Compliance
- Future of Sex Doll Regulation
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Countries Where Sex Dolls Are Illegal or Heavily Restricted
- Countries With Partial Bans or Severe Restrictions
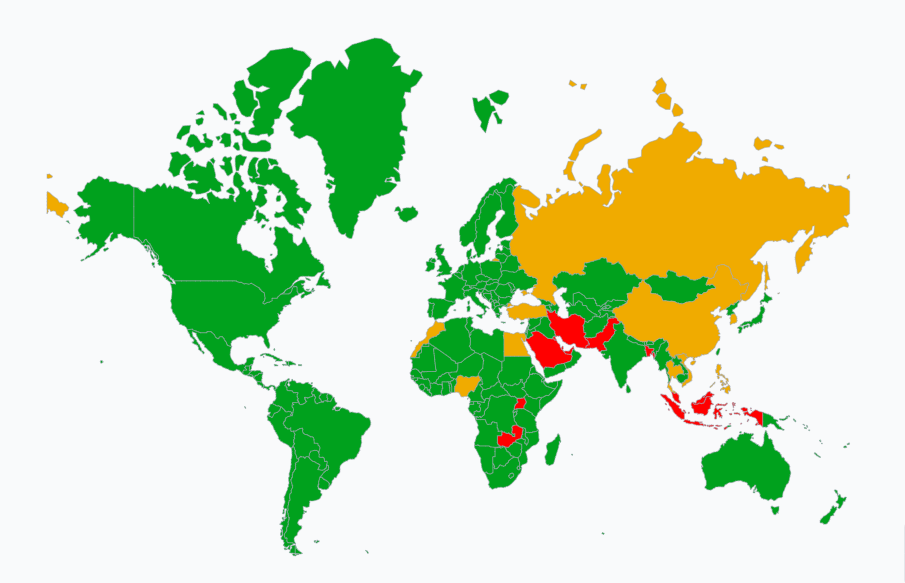
Navigating the legal landscape of sex doll ownership presents a complex challenge that varies dramatically across countries and regions. From outright bans in conservative nations to relatively permissive environments in countries like Japan, the legality of these products reflects diverse cultural, religious, and ethical perspectives worldwide. As realistic sex dolls become increasingly sophisticated and accessible, governments continue to develop and refine their regulatory approaches, often focusing on concerns ranging from child protection to public decency standards. This comprehensive guide explores the current legal status of sex dolls across different jurisdictions, highlighting key regulations, prohibited features, and potential legal risks for owners. Whether you’re curious about the laws in your own country or planning international travel, understanding these legal distinctions is essential for responsible ownership and compliance with local regulations.
Rise of Sex Dolls: Technology and Market Growth
The sex doll industry has undergone remarkable transformation in recent decades. What once began as simple inflatable products has evolved into sophisticated, anatomically detailed figures often featuring advanced materials like medical-grade silicone and thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). Some manufacturers have even integrated artificial intelligence, voice recognition, and heating elements to enhance realism.
This technological evolution has fueled significant market growth. Industry analysts estimate the global sex doll market to be worth billions, with consistent annual growth rates. Major manufacturers now operate across Asia, Europe, and North America, shipping products worldwide through increasingly mainstream distribution channels.
The normalization of these products has been accelerated by greater media coverage, celebrity endorsements, and their appearance in films and television shows. What was once an underground industry now operates increasingly in the open, though still subject to varying degrees of social stigma depending on location.
Legal and Ethical Controversies Worldwide
The growing availability and sophistication of sex dolls has prompted complex legal and ethical debates globally. These debates typically center around several key concerns:
First, child protection advocates raise alarm about dolls designed to resemble minors, arguing they could normalize harmful behaviors or serve as gateway products to actual abuse. This concern has driven much of the legislative response in Western countries.
Second, feminist perspectives are divided. Some argue these products objectify women and reinforce harmful sexual attitudes, while others contend they provide an outlet that doesn’t involve exploitation of actual people.
Third, religious and conservative viewpoints often frame these products as morally corrupting or contrary to traditional values regarding sexuality and relationships.
Finally, practical concerns about public decency, advertising standards, and appropriate regulation of an industry involving intimate products have prompted varied legislative responses.
These controversies have resulted in a remarkably diverse global patchwork of laws and regulations that potential owners must navigate carefully.
Understanding Sex Doll Legality: Global Overview
Legal Status Spectrum: From Full Acceptance to Total Prohibition
The global legal landscape for sex dolls exists on a spectrum. At one extreme, countries like Japan have few specific restrictions on ownership, allowing a thriving domestic industry. In the middle, nations like the United States and many European countries permit adult ownership but impose restrictions on certain features or public display. At the other extreme, several Middle Eastern and some African nations impose complete bans, with penalties including significant fines or imprisonment.
This spectrum reflects different cultural approaches to sexuality, religious influences on legislation, and varying governmental priorities regarding public morality versus personal freedom.
Key Legal Concerns Driving Regulation
Three primary concerns drive most sex doll regulation worldwide:
Child Protection Concerns: The most universally accepted restriction involves dolls designed to resemble minors. Many nations have explicit bans on child-like sex dolls, often extending existing child exploitation material laws to cover these products. The justification typically centers on preventing normalization of harmful attitudes toward children.
Public Decency Considerations: Many jurisdictions restrict public display, marketing, or advertising of sex dolls. These regulations aim to prevent exposure of such products to minors or unwilling adults. In some regions, regulations may control shop locations, window displays, or online marketing approaches.
Safety and Material Standards: Increasingly, countries are implementing consumer safety regulations specific to these products. These standards typically address chemical composition, potential allergenic materials, and durability concerns. In the European Union, for instance, products must meet specific toxicity and flammability standards.
Understanding these core regulatory concerns helps predict how different jurisdictions might approach sex doll legality, even when specific laws have not yet been enacted.
North American Sex Doll Legislation
United States Legal Framework
The United States offers a particularly complex regulatory environment due to its federal system. While no federal law explicitly bans adult sex dolls, several pieces of legislation impact their importation and distribution, particularly regarding child-like representations.
Federal Oversight and Legislation
The CREEPER Act (Curbing Realistic Exploitative Electronic Pedophilic Robots Act) was introduced in 2017 to ban importation and distribution of child-like sex dolls and robots. Though it passed the House of Representatives, it stalled in the Senate. Its successor, the JUSTICE Act (Jurists United to Stop Trafficking Imitation Child Exploitation Act), continued these efforts but has yet to become law.
Despite the lack of specific federal legislation, U.S. Customs and Border Protection frequently seizes child-like sex dolls under existing obscenity laws. These seizures have established a de facto import ban on certain products, even without explicit legislation.
State-by-State Legal Analysis
Individual states have increasingly enacted their own legislation regarding sex dolls:
Florida enacted a law in 2019 specifically criminalizing the possession of child-like sex dolls, with violations constituting a third-degree felony for first offenses and second-degree felonies for subsequent violations.
Tennessee passed similar legislation in 2019, explicitly banning the sale or possession of child-like sex dolls.
Kentucky, South Dakota, and Mississippi have all considered comparable bans, with varying degrees of legislative progress.
For adult sex dolls without child-like features, the legal landscape is generally more permissive. However, owners should be aware of varying state laws regarding obscenity, public decency, and specific product restrictions that might apply even to adult-oriented products.
Canada’s Approach to Sex Doll Regulation
Canada takes a notably different approach from its southern neighbor. While adult sex dolls are generally legal for personal use, Canada has explicitly banned child-like sex dolls under its child pornography laws. The Criminal Code of Canada defines child pornography to include “any material that visually depicts a person who is or is depicted as being under the age of eighteen years and is engaged in or is depicted as engaged in explicit sexual activity.”
Canadian Border Services Agency actively enforces these prohibitions, regularly seizing prohibited imports. Several high-profile cases have resulted in criminal charges against importers of child-like dolls, establishing clear legal precedent.
Mexico and Other North American Jurisdictions
Mexico currently lacks specific legislation addressing sex dolls. This regulatory vacuum has resulted in a generally permissive environment, though importation may still face challenges under general customs regulations regarding obscene materials.
Throughout the Caribbean and Central America, explicit legislation is similarly rare, with enforcement typically falling under broader obscenity or public decency laws rather than doll-specific regulation.
European Sex Doll Laws
European Union Standards and Cross-Border Considerations
The European Union’s common market creates unique regulatory complexities. While the EU hasn’t established specific union-wide legislation regarding sex dolls, several EU-wide standards indirectly impact the industry:
Product safety directives require non-toxic materials and proper labeling. Child protection laws generally prohibit child-like representations across all member states. Free movement of goods principles generally allow legal products to move between member states, creating challenges for countries wishing to impose stricter standards.
The resulting environment allows significant regulatory variation between member states while maintaining certain baseline standards across the continent.
Western Europe
United Kingdom: Following Brexit, the UK has maintained strict standards regarding sex dolls. UK law focuses particularly on height and feature requirements to prevent child-like representations. Border Force officials have authority to seize dolls they consider obscene or resembling children, resulting in numerous confiscations. Marketing restrictions also limit how these products can be advertised, with strict oversight from the Advertising Standards Authority.
France: French approaches center on moral standards and protection of minors. While adult sex dolls remain legal, child-like representations are strictly prohibited. Material safety standards apply, requiring products to meet EU and French-specific toxicity standards. Recent legislative discussions have considered imposing additional restrictions, though no major changes have yet been enacted.
Germany: Germany’s regulatory approach emphasizes data protection, particularly for newer AI-enabled products. The German regulatory framework addresses privacy concerns related to data collection by interactive dolls, requiring manufacturer compliance with strict data protection standards. As with other Western European nations, child-like dolls are prohibited, though adult products face few restrictions beyond standard product safety requirements.
Southern Europe
Spain and Italy both approach sex doll regulation through moral and ethical frameworks. Spain restricts public display and imposes advertising limitations but generally permits private ownership of adult products. Italy similarly focuses on material and ethical standards, with particular emphasis on preventing offense to public sensibilities through inappropriate display or marketing.
Northern Europe
The Netherlands has one of Europe’s most permissive approaches to sex dolls, consistent with its generally liberal attitudes toward adult products. However, even here, child-like representations are strictly prohibited. Display restrictions apply, particularly regarding visibility from public spaces.
Scandinavian countries generally permit adult sex dolls while maintaining strict provisions against child-like representations. Their regulatory approaches typically emphasize consumer protection and product safety standards rather than moral restrictions on adult products.
Eastern European Regulations
Eastern European approaches vary significantly. Some countries maintain minimal regulation, while others have imposed stricter standards, often reflecting conservative social attitudes. Poland, Hungary, and several Balkan nations have considered or implemented restrictions beyond the EU minimum standards, particularly regarding public display and advertising.
The diversity of European approaches reflects the continent’s varying cultural attitudes toward sexuality, differing religious influences, and distinct legal traditions.
Asia-Pacific Sex Doll Regulations
East Asia
Japan: Japan maintains perhaps the world’s most permissive regulatory environment regarding sex dolls. Few specific restrictions exist beyond standard product safety requirements. The Japanese industry has flourished in this environment, developing cutting-edge materials and technologies. While concerns about child-like representations exist, specific prohibitions remain limited compared to Western nations. Advertising guidelines do exist, however, requiring appropriate placement and content warnings.
China: Despite being a major manufacturing hub for these products, China imposes strict domestic controls. Chinese regulations prohibit brothels featuring sex dolls, with several high-profile enforcement actions against such establishments in recent years. Advertising faces significant restrictions, with prohibitions on public display and strict online marketing limitations. Export-oriented manufacturing continues to thrive despite these domestic restrictions.
South Korea and Taiwan: Both nations have developed regulatory frameworks positioning them between Japan’s permissive approach and China’s restrictions. South Korea explicitly bans child-like representations while permitting adult products. Taiwan similarly allows adult products while restricting certain features and marketing approaches.
Southeast Asia Regulatory Framework
Southeast Asian regulations vary dramatically, often reflecting religious and cultural differences within the region.
Thailand and the Philippines maintain relatively permissive environments, though both prohibit child-like representations.
Malaysia and Indonesia, with their predominantly Muslim populations, impose significant restrictions, often under broader morality or religious decency laws.
Singapore provides a distinctive middle ground, permitting private ownership while strictly regulating public display and marketing.
Australia and New Zealand
Australian State-by-State Differences: Australia’s federal system creates regulatory variation similar to the United States. Western Australia and Queensland have implemented specific restrictions on certain doll features. Most Australian states prohibit sex doll brothels, with several enforcement actions against businesses attempting to establish such venues. Federal customs authorities actively enforce prohibitions against child-like dolls, regularly seizing imports that violate these standards.
New Zealand Legislation: New Zealand maintains comprehensive legislation covering materials and advertising. The country explicitly categorizes child-like sex dolls as child exploitation material, imposing serious penalties for importation or possession. Adult products remain legal but subject to specific material safety standards and advertising restrictions.
Middle East, Africa, and Other Regions
Middle Eastern Prohibitions
Most Middle Eastern nations impose complete bans on sex dolls, regardless of features or representations. These prohibitions typically derive from religious principles and cultural values regarding sexuality and public morality.
Religious and Cultural Foundations of Bans: In Saudi Arabia, UAE, Qatar, and similar nations, Islamic principles regarding modesty and appropriate sexual expression form the foundation of these prohibitions. Religious authorities often explicitly condemn such products as immoral or contrary to religious teachings.
Penalties and Enforcement Mechanisms: Enforcement can be severe, with penalties including significant fines, imprisonment, and deportation for non-citizens. Customs authorities in these nations are particularly vigilant about preventing importation, regularly confiscating prohibited items at borders.
African Legal Landscape
Zambia and Other Countries with Strict Prohibitions: Several African nations maintain explicit bans. Zambia made international headlines by imposing particularly severe penalties for sex doll ownership or importation. Official statements linked these prohibitions to concerns about moral corruption and traditional values.
Varying Approaches Across the Continent: Africa’s regulatory landscape shows significant variation. While many nations maintain strict prohibitions similar to Zambia, others have not yet developed explicit legislation addressing these products. Enforcement often depends on general obscenity or public decency laws rather than doll-specific regulations.
South Africa presents a notable exception, with a legal approach more similar to Western nations—permitting adult products while prohibiting child-like representations. This reflects South Africa’s constitutional emphasis on personal freedoms balanced against public interests.
South American Legislation
South American approaches typically reflect the region’s predominant Catholic cultural influence while balancing modernizing attitudes toward sexuality. Brazil, the region’s largest market, permits adult products but restricts certain features and advertising approaches. Argentina similarly allows adult products while maintaining prohibitions on child-like representations.
Other South American nations generally lack explicit legislation, resulting in regulation through broader obscenity or import regulations rather than product-specific laws.
Key Legal Issues and Prohibited Features
Physical Characteristics Subject to Regulation
Height and Size Restrictions: Many jurisdictions establish minimum height requirements to prevent child-like representations. These standards typically specify that dolls must be at least 140-150cm tall (approximately 4’7″ to 4’11”) to comply with legal requirements.
Anatomical Features Under Scrutiny: Beyond overall size, specific anatomical features may trigger regulatory concerns. Several jurisdictions prohibit products with dimensions suggesting immaturity rather than adult development.
Child-Like Representations: Universal Red Line: The prohibition against child-like representations represents the most widely accepted regulatory standard globally. While definitions of what constitutes a “child-like” representation vary, this prohibition exists in almost all jurisdictions that permit adult products.
Material and Safety Standards
Chemical Composition Requirements: Regulators increasingly focus on material safety, prohibiting harmful chemicals like certain phthalates commonly used as plasticizers. EU regulations have been particularly influential in establishing global standards for material composition.
Manufacturing Guidelines: Some jurisdictions impose manufacturing standards addressing durability, structural integrity, and potential health risks. These standards aim to prevent injuries and ensure products can be cleaned adequately to prevent bacterial growth.
Technology-Related Regulations
AI and Interactive Features: As dolls incorporate more technology, new regulatory questions emerge. Data protection laws may apply to AI-enabled products that collect user information. Some jurisdictions have begun developing specific standards for interactive capabilities.
Data Privacy Concerns: Products with recording capabilities, internet connectivity, or user data storage face increasing regulatory scrutiny. The EU’s GDPR and similar privacy regulations worldwide may apply to manufacturers and distributors of technologically enhanced products.
Prohibited Activities by Region
Production and Manufacturing Restrictions: In regions with complete bans, production and manufacturing are typically prohibited. Even in more permissive environments, manufacturing may face specific licensing requirements or location restrictions.
Import/Export Controls: Border controls represent a primary enforcement mechanism in many jurisdictions. Customs authorities often have broad discretion to seize products they consider obscene or prohibited, even in regions lacking explicit legislation.
Public Display and Marketing Limitations: Even jurisdictions permitting private ownership frequently restrict public display and advertising. These restrictions typically aim to prevent exposure to minors or unwilling adults.
Commercial Use Restrictions (Brothels): Sex doll brothels face widespread prohibition, even in regions permitting private ownership. Several countries have enacted specific legislation following attempts to establish such businesses.
Consumer Guide: Ensuring Legal Compliance
Pre-Purchase Legal Checklist
Before purchasing a sex doll, consumers should:
- Research specific laws in their jurisdiction regarding permissibility and prohibited features
- Verify the manufacturer complies with relevant height, material, and feature requirements
- Ensure the retailer operates legally and ships to their location
- Confirm the product doesn’t incorporate prohibited features like child-like representations
- Review any technology features for compliance with local data protection laws
Documentation and Customs Considerations
When importing products:
- Maintain clear documentation proving the product meets adult size requirements
- Consider whether manufacturer certification or documentation addresses legal compliance
- Be aware that customs officials often have broad discretion regarding seizure of products they consider obscene
- Understand that even if technically legal, products may face significant import challenges
- Research specific customs procedures and potential tariffs or taxes
Legal Risks Assessment Framework
Potential owners should assess legal risks along several dimensions:
- Explicit prohibitions in local law
- Enforcement history in their jurisdiction
- Potential penalties if found non-compliant
- Privacy considerations regarding purchase and delivery
- Future regulatory changes based on legislative trends
Storage and Disposal Legal Considerations
Ownership responsibilities extend beyond purchase:
- Store products away from public view to comply with display restrictions
- Consider privacy implications of maintenance or repair services
- Research proper disposal methods compliant with local waste management regulations
- Understand legal implications of reselling used products, which may be prohibited in some jurisdictions
- Consider potential customs issues when moving internationally with such products
Future of Sex Doll Regulation
Emerging Legislation and Proposed Changes
Several regulatory trends appear likely to shape future legislation:
- Increasing focus on AI and data protection as products incorporate more technology
- Greater standardization of material safety requirements
- More explicit prohibitions against child-like representations
- Potential integration with broader sex work or prostitution legislation
- Growing distinction between private ownership and commercial use in regulatory approaches
Technology Advancements Driving New Legal Questions
Advancing technology creates new regulatory challenges:
- AI systems raising questions about consent, representation, and appropriate programming
- VR integration creating potential new categories for regulation
- Increasingly realistic appearance blurring lines regarding public display standards
- Remote control features raising jurisdictional questions about who controls the product
- Integration with other services creating novel regulatory categories
Advocacy and Industry Self-Regulation Efforts
The industry increasingly recognizes the importance of responsible self-regulation:
- Industry associations developing voluntary standards to prevent restrictive legislation
- Manufacturer cooperation with reasonable safety and feature requirements
- Marketing standards aiming to maintain acceptable public perception
- Privacy-focused design approaches addressing data protection concerns
- Engagement with lawmakers to develop balanced regulatory approaches
Conclusion
Global Trends in Sex Doll Regulation
The global regulatory landscape continues to evolve, with several clear patterns emerging:
Near-universal prohibition of child-like representations represents perhaps the strongest international consensus.
Most jurisdictions distinguish between private ownership and public display or commercial use, with stricter standards for the latter.
Material safety and consumer protection standards increasingly complement or replace moral prohibitions in many Western nations.
Cultural and religious factors remain powerful determinants of regional approaches, creating a diverse global regulatory environment.
Responsible Ownership Guidelines
Responsible ownership includes:
Understanding and complying with local legislation Maintaining appropriate privacy and discretion Ensuring proper storage away from public view or access by minors Verifying products meet material safety standards for personal health Proper maintenance and eventual disposal according to local regulations
Resources for Staying Informed on Changing Laws
As laws continue to evolve, owners should:
- Monitor relevant legislation in their jurisdiction
- Consider consulting legal professionals for specific advice
- Join owner communities that share regulatory updates
- Follow industry news sources for changing standards
- Review manufacturer communications regarding compliance issues
Frequently Asked Questions
General Legality Questions
Are sex dolls legal generally? Adult sex dolls are legal in many countries for private use, though specific restrictions vary widely. The most common prohibitions involve child-like representations, public display, and commercial use in brothel-type establishments.
What features make a sex doll illegal in most places? Child-like appearances represent the most universally prohibited feature. This may include height restrictions, proportions suggesting immaturity, or marketing suggesting youth. Some jurisdictions also restrict certain technological features, particularly those raising privacy concerns.
How do religious values impact sex doll legality? Countries with strong religious influence in governance typically impose stricter regulations or complete bans. This is particularly evident in conservative Muslim-majority nations and some predominantly Catholic countries, where religious principles often explicitly inform legislation.
US-Specific Legal Questions
Is there a federal law against sex dolls in the US? No specific federal law comprehensively regulates adult sex dolls, though the proposed CREEPER Act and JUSTICE Act aimed to prohibit child-like representations. Currently, regulation occurs primarily through state legislation, customs enforcement, and general obscenity laws.
How do state laws differ regarding sex doll ownership? States like Florida, Tennessee, and Kentucky have enacted specific legislation prohibiting child-like sex dolls. Other states rely on general obscenity statutes or consumer protection laws. Some states impose no specific restrictions beyond federal standards.
What is the legal status of importing sex dolls to the US? Importing adult sex dolls is generally permitted, though customs officials have broad discretion to seize items they consider obscene. Child-like dolls are consistently seized under existing obscenity laws even without explicit federal legislation.
International Transport and Travel Questions
Can I legally travel internationally with a sex doll? International travel with sex dolls presents significant legal risk due to varying laws and customs officials’ broad discretion. Even countries permitting ownership may restrict importation or subject such items to extensive examination.
Are there countries where bringing a sex doll would result in legal penalties? Yes, numerous countries—particularly in the Middle East, parts of Asia, and some African nations—impose severe penalties for importing sex dolls. These may include fines, imprisonment, and deportation for non-citizens.
Age Restrictions for Owners and Representations
Is there a minimum age to purchase sex dolls? Most jurisdictions restricting sales of sex dolls impose minimum age requirements consistent with other adult products, typically 18 or 21 years. Online retailers generally implement age verification systems to comply with these requirements.
How do regulators determine if a doll has child-like features? Regulatory determinations typically consider height (usually requiring minimum 140-150cm), proportions, facial features, and marketing materials. Some jurisdictions have developed specific guidelines, while others rely on case-by-case assessment by customs or law enforcement officials.
Countries Where Sex Dolls Are Illegal or Heavily Restricted
Country/Region |
Legal Status |
Key Restrictions |
Penalties |
|---|---|---|---|
Saudi Arabia |
Prohibited |
Complete ban on all sex dolls |
Confiscation, fines, possible imprisonment |
United Arab Emirates |
Prohibited |
Complete ban under morality laws |
Confiscation, fines, imprisonment, possible deportation for non-citizens |
Qatar |
Prohibited |
Complete ban under religious grounds |
Confiscation, fines, imprisonment |
Kuwait |
Prohibited |
Complete ban |
Confiscation, potential detention |
Iran |
Prohibited |
Complete ban under morality laws |
Severe penalties including possible imprisonment |
Zambia |
Prohibited |
Explicit nationwide ban announced in 2018 |
Confiscation, potential criminal charges |
Uganda |
Prohibited |
Banned under anti-pornography legislation |
Confiscation, potential fines |
Malaysia |
Prohibited |
Banned under religious and morality grounds |
Confiscation, potential fines |
Indonesia |
Prohibited |
Banned under anti-pornography laws |
Confiscation, fines, potential imprisonment |
Pakistan |
Prohibited |
Banned under obscenity laws |
Confiscation, potential fines |
Bangladesh |
Prohibited |
Banned under conservative morality laws |
Confiscation, potential legal consequences |
Brunei |
Prohibited |
Complete ban under Sharia law |
Severe penalties, confiscation |
Maldives |
Prohibited |
Banned under religious grounds |
Confiscation, potential legal consequences |
Some Indian states |
Varies by state |
Prohibited in conservative states under obscenity laws |
Confiscation, potential fines |
Countries With Partial Bans or Severe Restrictions
Country/Region |
Legal Status |
Key Restrictions |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
China |
Restricted |
Brothels using dolls banned, strict advertising controls |
Manufacturing for export continues despite domestic restrictions |
South Korea |
Restricted |
Child-like dolls explicitly banned, customs seizures common |
Adult dolls technically permitted but face frequent import challenges |
Thailand |
Restricted |
Restrictions on public display and certain features |
Private ownership generally tolerated |
Russia |
Restricted |
Increasing restrictions, particularly on child-like representations |
Regulations continue to evolve |
Philippines |
Restricted |
Restrictions on import and certain features |
Enforcement varies significantly |
Vietnam |
Restricted |
Restrictions under public morality laws |
Enforcement inconsistent |
Turkey |
Restricted |
Significant import restrictions, religious objections |
May be seized at customs despite lack of explicit ban |
Egypt |
Prohibited/Restricted |
Generally prohibited under morality laws |
Religious and cultural prohibitions enforced |
Morocco |
Restricted |
Severe import restrictions, cultural prohibitions |
Often seized during import |
Nigeria |
Varies |
Restrictions in northern states with Sharia law |
Southern regions generally more permissive |
Important Notes:
- Law vs. Enforcement: In many countries, explicit legislation may not exist, but prohibition occurs through customs enforcement, general morality laws, or religious decrees.
- Changing Landscape: Regulations continue to evolve globally, with many countries developing more specific legislation as these products become more widely available.
- Child-like Representations: Even in countries where adult sex dolls are legal, child-like representations are almost universally prohibited. This table focuses on restrictions on all types of sex dolls.
- Verification Recommended: Before attempting to import or possess sex dolls in any country, verify current laws directly with official sources, as enforcement practices can change more rapidly than formal legislation.
- Regional Variations: Some countries have significant internal variation in enforcement, particularly in federalized nations or those with strong regional governments.
This information is provided for educational purposes only and should not be considered legal advice. Always consult with qualified legal professionals regarding specific situations in your jurisdiction.

